Configuring GrowthBook to work with Matomo
GrowthBook makes it easy to do A/B testing using Matomo as an event source. This guide shows you how to set up GrowthBook to work with self-hosted Matomo and the MySQL/MariaDB that it runs on.
1. Integrate GrowthBook's SDK with Matomo within your application
You can follow the SDK integration guides depending on your language. We need to add the TrackingCallback call
specifically for Matomo. For this guide, we'll use Javascript (Next.js).
Matomo lets you track custom events, and you can adjust the Event Category, Event Action, Event Name, and
Event Value. You can read more about the custom tracking call at Matomo's documentation site.
- Event Category cannot contain any spaces.
- If Event Name is 0 or "0" it will record null.
- Event Value must be an integer.
To work with the default data schema in GrowthBook, we will encode the following:
Event Category: will have the valueExperimentViewedto isolate the exposure events.Event Action: will store the experiment key.Event Name: will store the variation id (with a prefix ofvor some other string)
// Create a GrowthBook instance
const growthbook = new GrowthBook({
trackingCallback: (experiment, result) => {
window["_paq"] = window._paq || [];
window._paq.push([
"trackEvent",
"ExperimentViewed",
experiment.key,
"v" + result.variationId,
]);
},
});
With that set, we need to load the user id into the GrowthBook user attributes. The following code shows how to do this with the Matomo anonymous visitor ID
// add the Matomo anonId when loaded
let visitor_id;
if ("_paq" in window) {
_paq.push([
function () {
visitor_id = this.getVisitorId();
growthbook.setAttributes({
...growthbook.getAttributes(),
id: visitor_id,
});
},
]);
}
For Next.js, we would need to do this in the useEffect and also detect the window in case of a server side render:
// Create a GrowthBook instance
const growthbook = new GrowthBook({
trackingCallback: (experiment, result) => {
if (window) {
window["_paq"] = window._paq || [];
window._paq.push(['trackEvent', 'ExperimentViewed', experiment.key, "v"+result.variationId]);
}
}
});
export default function MyApp({ Component, pageProps }) {
useEffect(() => {
// Load feature definitions from API
fetch(process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GROWTHBOOK_FEATURES_URL)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((json) => {
growthbook.setFeatures(json.features);
});
// TODO: replace with real targeting attributes
growthbook.setAttributes({
"company": "foo",
"browser": "foo",
"url": "foo"
});
// add the Matomo anonId when loaded
let visitor_id;
if("_paq" in window) {
_paq.push([function () {
visitor_id = this.getVisitorId();
growthbook.setAttributes({ ...growthbook.getAttributes(), id: visitor_id });
}]);
}
}, []);
...
2. Add the Data Source for Matomo
From within the GrowthBook application, navigate to the Data Sources page from within the Analysis section. Click on add data source and select MySQL/MariaDB.
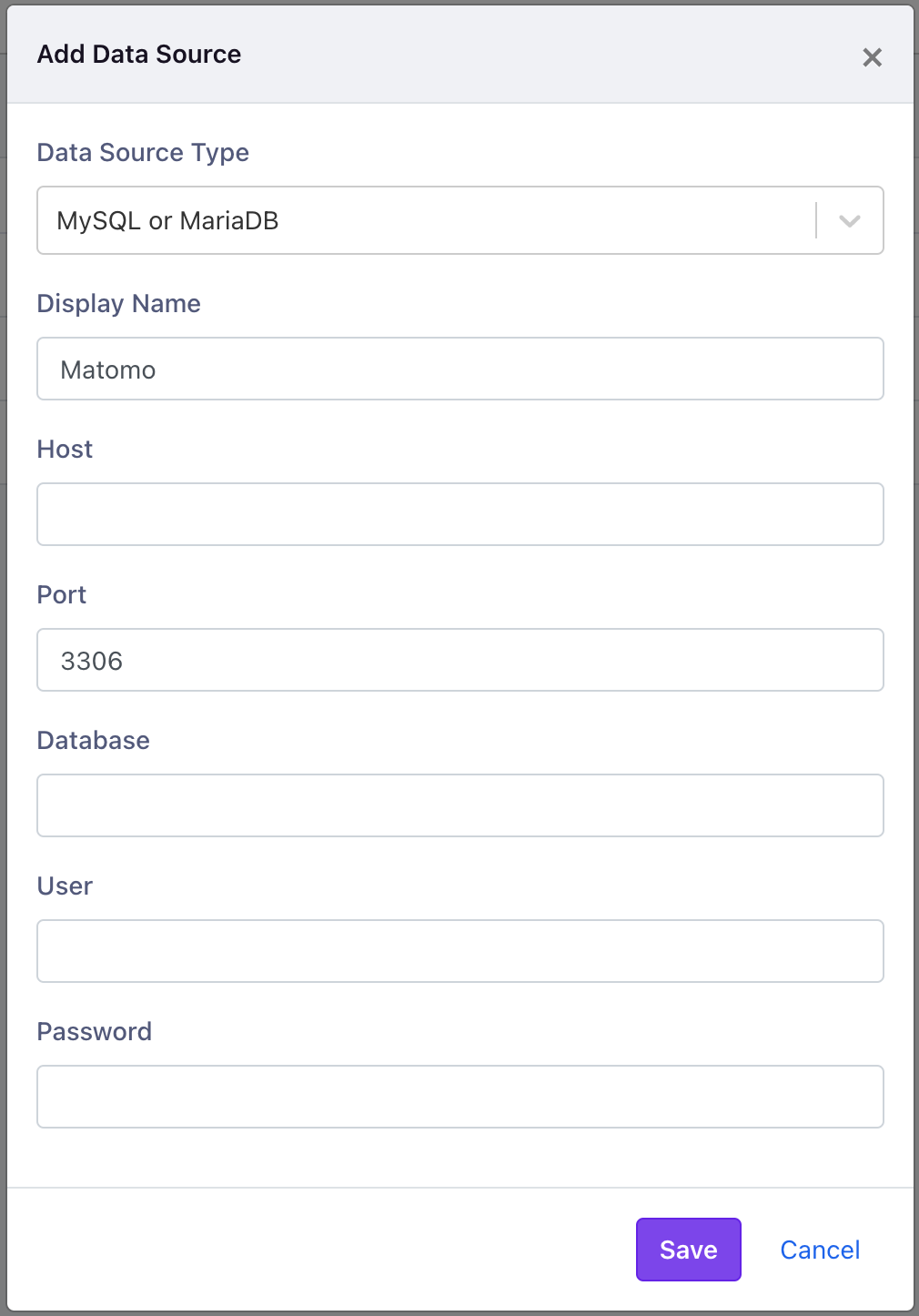
When you successfully connect to your Matomo data source, you will see the following:
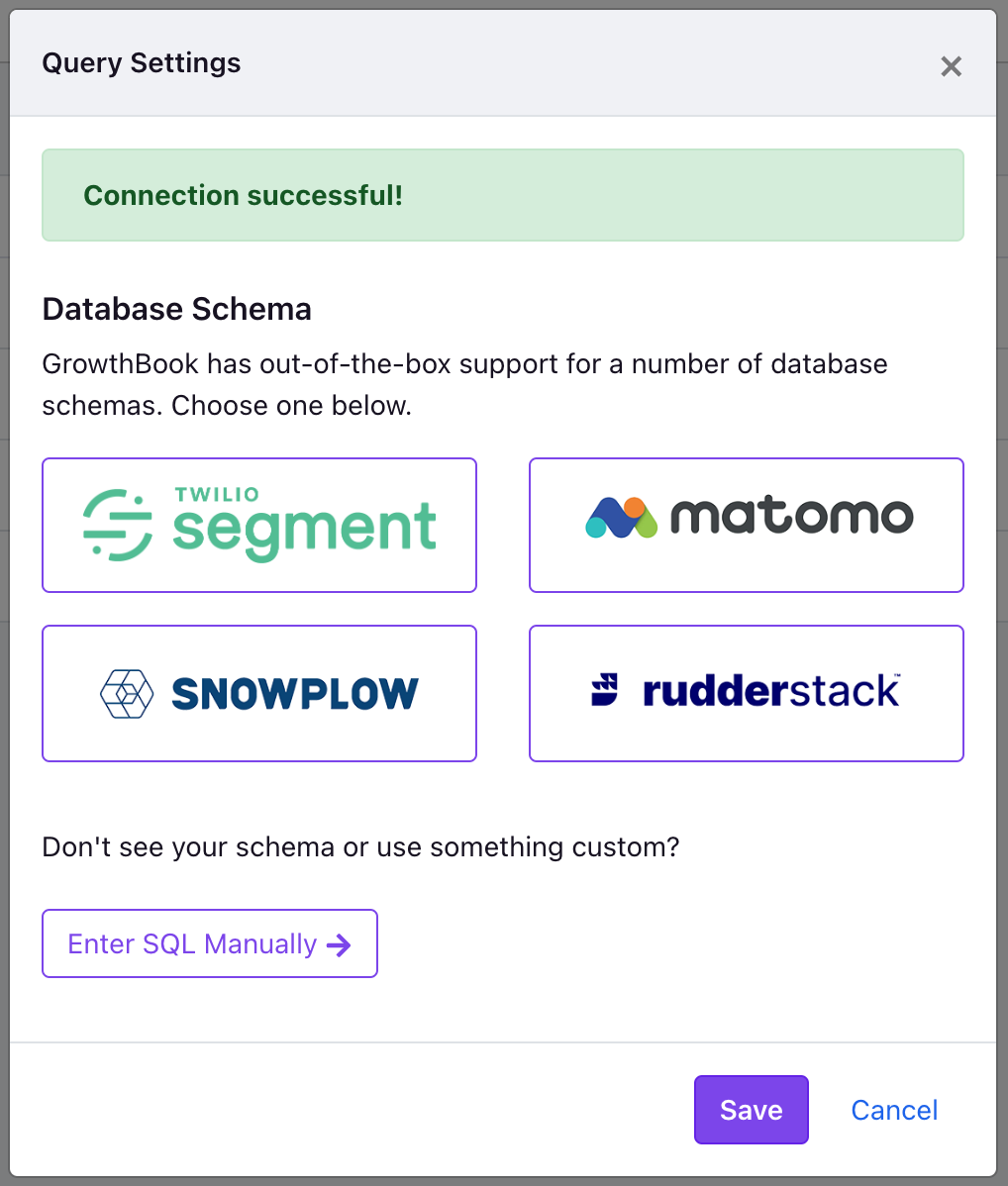
Select the Matomo schema from the list, and then you can adjust some settings specific to your instance and how you implemented the Matomo tracking code.

When you save, you'll have the experiment exposure queries for anonymous and user_id set for you.
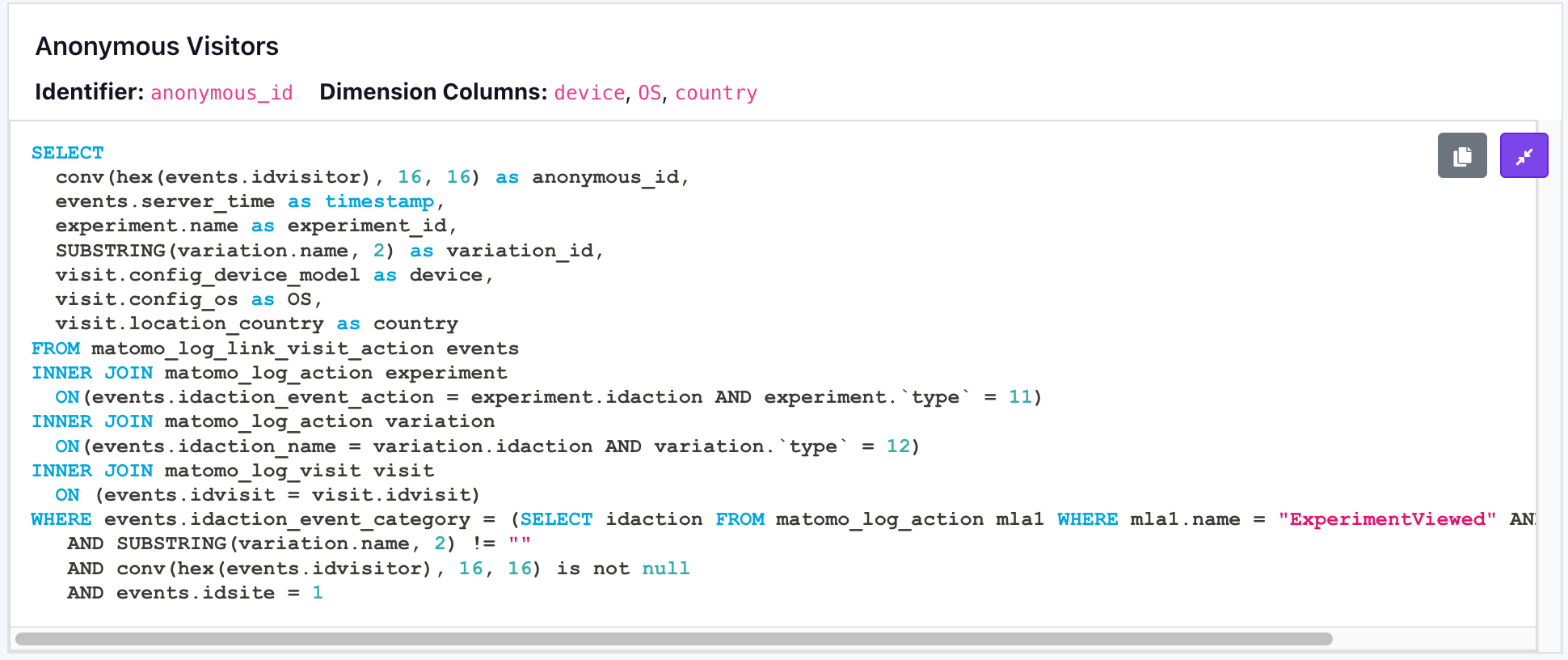
You can test running this query directly against your database. It should return a list of experiments exposure events.
You will still need to define the metrics you want to test against from the metrics settings.
